As Vietnamese students increasingly pursue education both domestically and abroad, understanding the Grade Point Average (GPA) system becomes essential. GPA serves as a critical metric that can influence academic opportunities, scholarship eligibility, and career prospects. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what GPA is, how it is calculated, its significance in various academic contexts, and the GPA conditions at some universities in the U.S.
What is GPA?
GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a standard way of measuring academic achievement in the U.S. educational system and in many other countries. It is a numerical representation of a student’s academic performance, typically on a scale from 0.0 to 4.0.
The Scale
- 4.0: Represents an “A” or excellent performance
- 3.0: Represents a “B” or good performance
- 2.0: Represents a “C” or average performance
- 1.0: Represents a “D” or below average performance
- 0.0: Represents an “F” or failing performance
In many institutions, an “A” is assigned 4 points, a “B” 3 points, a “C” 2 points, a “D” 1 point, and an “F” 0 points. Some schools use a weighted GPA system, where more challenging courses (like Advanced Placement or honors classes) are given additional points, allowing for a maximum GPA higher than 4.0.
How is GPA Calculated?
Understanding how GPA is calculated is crucial for students aiming to manage their academic performance effectively.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Assign Points: Each grade is converted to its corresponding point value.
- For example:
- A = 4 points
- B = 3 points
- C = 2 points
- D = 1 point
- F = 0 points
- For example:
- Multiply Points by Credits: Each course typically has a credit value (usually 3 or 4 credits for most classes).
- For instance, if you receive an “A” (4 points) in a 3-credit course, that contributes 12 points to your GPA (4 points x 3 credits).
- Sum Points and Credits: Add together all the grade points earned and the total credits attempted.
- Divide Total Points by Total Credits: Finally, divide the total grade points by the total credits to find your GPA.
- Example: If you earned 36 points over 12 credits, your GPA would be 3.0 (36 ÷ 12 = 3.0).
Example Calculation
Consider a student who completed the following courses:
| Course | Grade | Points | Credits | Total Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematics | A | 4.0 | 3 | 12 |
| English | B | 3.0 | 3 | 9 |
| History | C | 2.0 | 3 | 6 |
| Science | A | 4.0 | 4 | 16 |
Total Points: 12 + 9 + 6 + 16 = 43
Total Credits: 3 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 13
GPA: 43 ÷ 13 = 3.31
This student’s GPA would be approximately 3.31.
The Importance of GPA
GPA holds significant weight in various aspects of a student’s academic and professional journey.
Academic Opportunities
- College Admissions: For students applying to universities, especially in the U.S., a high GPA is often a crucial factor in admissions decisions. Most institutions have minimum GPA requirements, and competitive programs look for students with GPAs above the average.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Many scholarships consider GPA as a primary criterion. A higher GPA can unlock financial aid opportunities that make education more accessible.
- Honors Programs: Some schools offer honors programs or advanced courses that require a minimum GPA for enrollment. These programs often provide a more rigorous academic experience and can enhance a student’s educational profile.
The Impact of GPA in Vietnam
In Vietnam, the education system has its own grading scale, typically ranging from 0 to 10. However, as more Vietnamese students study abroad, especially in the U.S. or other Western countries, understanding and converting GPA is crucial.
Converting Vietnamese Grades to GPA
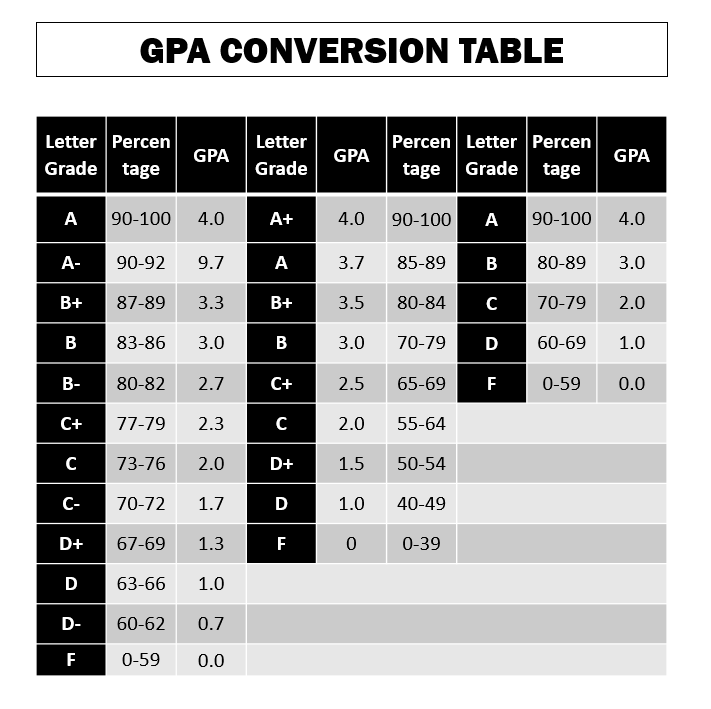
- Identify Equivalencies: Vietnamese grades can be converted to the GPA scale by establishing equivalents. Here’s a rough conversion:
- 9.0 – 10.0 = A (4.0)
- 8.0 – 8.9 = B (3.0)
- 7.0 – 7.9 = C (2.0)
- 6.0 – 6.9 = D (1.0)
- Below 6.0 = F (0.0)
- Use Conversion Tools: Many universities provide online tools or guidelines for converting grades to GPA. It’s crucial to check with specific institutions for their grading policies. Example:
https://www.scholaro.com/gpa-calculator/
https://www.calculator.net/gpa-calculator.html
GPA Conditions at Some U.S. Universities

| University | Minimum GPA Requirement | Average GPA for Admitted Students | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| University of California System | 3.0 (California residents), 3.4 (non-residents) | N/A | Extra points for honors/AP/IB courses allowed |
| Florida State University (FSU) | 3.0 (unweighted) | N/A | 3.6+ for automatic merit scholarship consideration |
| University of Southern California (USC) | 3.0 | ~3.7 | Higher requirements for specialized programs |
| New York University (NYU) | 3.0 | N/A | Holistic admissions process; considers extracurriculars and essays |
| Ivy League Schools (e.g., Harvard, Yale) | N/A | ~4.0+ (weighted) | Holistic review; GPA is important but not the sole factor |
| University of Michigan | 3.0 | ~3.8 | Competitive programs may require higher GPAs |
| University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign | 3.0 | ~3.7 | Different standards for specific programs |
| University of Texas at Austin | 3.0 | ~3.8 | High competition for popular majors |
| University of Washington | 2.0 (general), varies by program | ~3.5 | Strong emphasis on holistic review |
| Purdue University | 3.0 | ~3.6 | Engineering and certain programs may require higher GPAs |
| Georgia Institute of Technology | 3.0 | ~4.0 | Highly competitive for STEM programs |
| Northeastern University | 3.0 | ~3.6 | Co-op program enhances application appeal |
| Boston University | 3.0 | ~3.6 | Various programs have specific GPA expectations |
About weighted vs unweighted GPA: Understanding GPA: Weighted vs. Unweighted for Vietnamese Students
Common Questions About GPA
- What is a good GPA?
- A GPA of 3.0 is generally considered a passing average, but competitive programs often look for GPAs of 3.5 or higher. Ivy League schools may expect GPAs above 4.0 (weighted).
- How does a weighted GPA differ from an unweighted GPA?
- An unweighted GPA does not take the difficulty of courses into account (max 4.0), while a weighted GPA gives additional points for advanced courses (like honors or AP), potentially exceeding 4.0.
- How can I raise my GPA?
- Focus on improving grades in current and future classes, seek help when needed, and manage your time effectively. Retaking courses where you earned low grades may also help.
- Do all universities use the same GPA scale?
- No, while many use a 4.0 scale, some may use different scales or weighting systems. Always check the specific policies of each institution.
- How do extracurricular activities impact GPA?
- Extracurricular activities do not directly impact GPA, but they can enhance your overall application by demonstrating leadership and commitment, which may indirectly affect your admissions prospects.
- What happens if I fail a class?
- Failing a class typically results in a 0.0 for that course, which can significantly lower your GPA. Many schools allow you to retake courses, and the new grade may replace the failing grade in GPA calculations.
- How do universities view GPA in the admissions process?
- GPA is a critical factor, but admissions committees also consider standardized test scores, personal statements, letters of recommendation, and extracurricular involvement.
- Can I convert my GPA from a different system to the U.S. system?
- Yes, you can convert grades using established equivalencies, but it’s essential to check specific university guidelines for accurate conversions.
- How is GPA calculated for transfer students?
- Transfer students typically have their previous coursework evaluated, and GPAs from different institutions are often recalculated based on the new school’s scale.
- Is GPA the only factor in graduate school admissions?
- No, while a strong GPA is important, graduate programs also consider research experience, letters of recommendation, personal statements, and standardized test scores (like the GRE).
Conclusion
Understanding GPA is vital for Vietnamese students navigating both local and international education systems. A strong GPA can open doors to numerous academic and career opportunities, making it an essential component of your educational journey. By grasping how GPA works, its significance, and the specific conditions at various universities, students can take proactive steps toward achieving their academic goals.
As you embark on this journey, remember that education is not just about numbers; it’s also about growth, learning, and developing the skills necessary to thrive in an ever-changing world. With determination and the right approach, you can make your GPA a true reflection of your hard work and dedication.

Pingback: Unlock Your Potential: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses for a Successful US Study Abroad - hocbongusa.com